Tech
Why PeeringDB is Useful
PeringDB is an online database filled with information about Internet networks. This includes networks, physical locations where networks connect to one another and also Internet exchanges where networks peer with one another. To understand what PeeringDB is and why is it useful you must first understand what Internet peering is.
Basically, the Internet is a huge collection of multiple smaller networks. These networks all connect to one another in some form to create one huge network. This single huge network is called the Internet. Peering is one way in which individual networks connect to one another to create the Internet.
PeeringDB is an amazing tool because it allows networks to find and connect to each other. It also allows network architects to plan where to expand their network. Network architects and network administrators use the information from PeeringDB on a daily basis.
Finding New Peers
As stated earlier, the Internet is a collection of smaller networks. Each of these networks connects to other networks to form the Internet. Choosing who to connect to can be a difficult process. If you are in charge of a certain network you must decide who you should but IP transit from, and also who you should attempt settlement-free peering with.
PeeringDB provides a single website where to can find all the networks which are located in the same facility as your routers. This will present you with a full list of networks you can connect to. You can then click on the networks which are located in the same facilities as your routers and find out which best suits your IP transit and peering needs.
Expanding To New Locations
Successful networks grow. If you are looking to grow your network you must find new locations to expand to. PeeringDB provides a list of common networking facilities and a list of peering exchange points. You can search through the site by state or country to find all the locations and exchange points which you can expand into.
One you have a list of potential facilities and exchanges, the next step is to look at all the networks that currently exist in those locations. Specifically, you are usually looking for new networks to peer with, or new networks to buy IP transit from. It doesn’t make sense to physically expand your network to a location that does not have any new connections.
Not only does PeeringDB list the networks at each location, it often provides the peering policy of those networks. You can see if those potential peers have an open or closed peering policy. Expanding into a new location where all the networks have a closed peering policy will not lead to many new connections.
Judging Other Networks
There are a number of ways to judge how large a network is. The number of public and private peering exchange points that the network connects to is one such way. The more exchange points a network is located in, the higher its connectivity will be. PeeringDB provides a list of both public and private peering locations for networks.
It also provides traffic levels, IPv4 and IPv6 prefix numbers, the geographic scope, etc.
Basically, PeeringDB is the place to go to find out information about other networks. This can be useful not only for potential peers, but also to judge how your competition is doing. You may be interested in seeing where your competition has connections. Are they in a location where you are not?
If you interact with other networks or need information about other networks or networking locations, PeeringDB is a great place to start.
Tech
From Dream to Deployment: The Tools Designers Actually Use Today (and What You Can Learn)
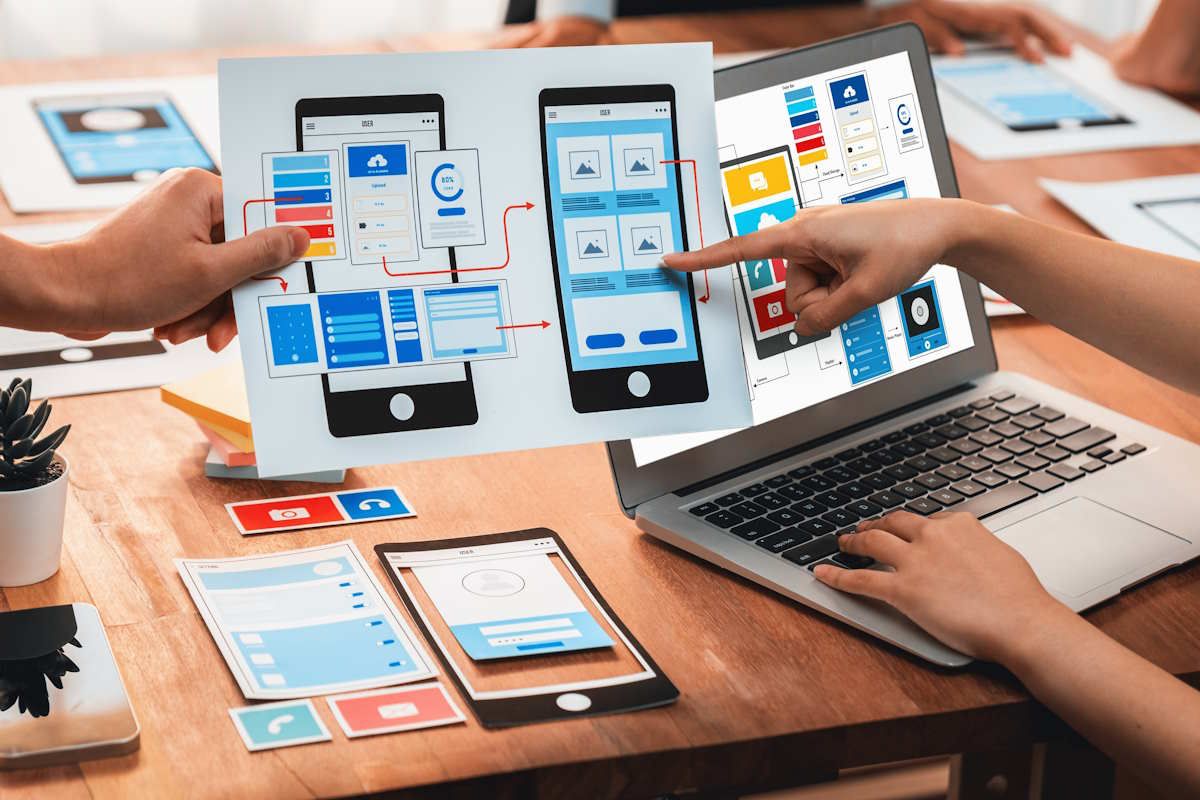

Let me tell you something from the front lines: you haven’t truly experienced modern website design until you’ve watched a front-end dev cry tears of joy (or despair) over their Figma-to-code handoff. Or a designer whispers sweet nothings to their Adobe Firefly-powered layer mask. Welcome to 2025, where Designer Tools websites are no longer static pages—they’re living, breathing pieces of a brand’s DNA. And in Columbia, South Carolina, that shift is more alive than ever.
I’ve followed the evolution of design tooling over the past decade like a caffeine-fueled detective tracking breadcrumbs on a codebase. It’s been a ride from our beloved early-days Adobe Photoshop slicing era to the rise of auto-layouts and AI-powered mockups. Companies like Web Design Columbia (WDC) haven’t just kept up—they’ve quietly led the charge for businesses that want smart, affordable websites without Silicon Valley drama.
This article is about peeling back the curtain. No, not to expose some sketchy markup. But to dive into the actual tools used by experienced designers today, and to show you how those tools impact not only how your site looks, but how well it performs and grows.
Figma Took Over the World (But It’s Not Always Perfect)

It’s impossible to talk about modern design workflows without bowing slightly toward Figma. Once considered a “Google Docs for designers,” Figma has now become the backbone of collaborative design around the globe. Adobe thought it was such a threat that they tried to buy it for $20 billion. (That deal? Blocked. Thank you, antitrust laws.)
Figma has been a game-changer in Columbia, SC, particularly for a web design company like WDC. Designers, developers, marketers—even the “just-make-it-red” stakeholders—can all peek into one live file, reducing miscommunications, mismatched margins, and mysterious pixel drifts. Figma supports auto-layouts, component libraries, prototyping, and plugins galore.
But even Figma has its quirks. For example, when you push a complex Figma design into actual code, things get… spicy. Those beautiful nested auto-layouts don’t always translate cleanly into responsive CSS. And while Figma’s prototyping tools are sleek, they still don’t fully simulate real-world performance—something I’ve heard engineers at WDC wrestle with regularly.
Firefly and the Era of AI-Enhanced Design
Let’s talk about Adobe Firefly for a second. If you haven’t heard, Adobe’s venture into generative AI allows designers to type design elements into existence. Want a button styled like a 1970s sci-fi novel cover? Firefly can do that. Need a header background that matches the vibe of a luxury whiskey brand? Boom—prompt, click, done.
Firefly isn’t just a gimmick—it’s being used globally. According to Adobe’s 2024 Creative Trends report, over 43% of professional designers now incorporate generative AI in at least one part of their workflow. That includes agencies in Tokyo, freelancers in São Paulo, and even teams here in Columbia, South Carolina.
Web Design Columbia uses Firefly not to replace humans but to amplify them. For example, they might use it to generate mock content blocks or texture patterns, then refine those with a designer’s eye. But even with its strengths, Firefly isn’t magic. AI-generated elements still need to be optimized, especially for loading speeds and accessibility compliance, two things WDC takes very seriously.
The Great Divide: Designing for Desktop vs Mobile
Here’s a brutal truth about design in 2025: if your site isn’t built mobile-first, you’re leaving traffic—and revenue—on the table. Google’s mobile-first indexing, which began rolling out in 2018, is now fully enforced. Nearly 59% of web traffic worldwide comes from mobile devices (Statista, 2024), and that number climbs every year.
This mobile shift has made tools like Webflow more popular than ever. Webflow is a visual web development platform that lets you build responsive websites with near pixel-perfect precision. It’s like the love child of Figma and HTML/CSS. But here’s the kicker—many designers still misuse it.
Inexperienced teams may lean too heavily on drag-and-drop templates without understanding the semantic structure of HTML, leading to accessibility issues and bloated code. That’s where experienced companies, like WDC, pull ahead. With nearly 20 years in the game, their designers and developers don’t just make it look good—they make sure it runs lean, passes Lighthouse audits, and doesn’t choke your user’s phone on a 3G connection.
If you’re looking for some website design insights rooted in actual experience, that’s where their legacy becomes a big deal.
Three.js, Spline, and the Rise of 3D Web Experiences
Here’s something I never thought I’d say in a client meeting: “Yes, we can make your website spin a 3D donut on hover.” And I’m not joking. Welcome to the age of WebGL-powered visuals and 3D modeling tools like Three.js and Spline.
Three.js, a JavaScript library, has become the gold standard for rendering interactive 3D on websites. Big names like Google, BMW, and even NASA use it for space simulations. Spline, on the other hand, makes it approachable—even for teams that don’t code. It allows designers to craft real-time, responsive 3D experiences and export them straight to the web.
A web design company in Columbia, SC, using these tools? You better believe it. Web Design Columbia has used Spline to let customers visually customize room setups, car paint jobs, or even event venues. Imagine a furniture store that lets you virtually arrange chairs around a table before buying—now that’s engagement. But it comes with challenges: 3D assets are heavy, load times can spike, and compatibility across devices is still hit-or-miss, especially on older mobile hardware.
That’s why WDC often builds fallback versions and ensures that performance isn’t sacrificed for flair. Impressing a user with 3D is one thing—it’s another to keep them around long enough to convert.
The Silent Hero: Git and Version-Control-Driven Design
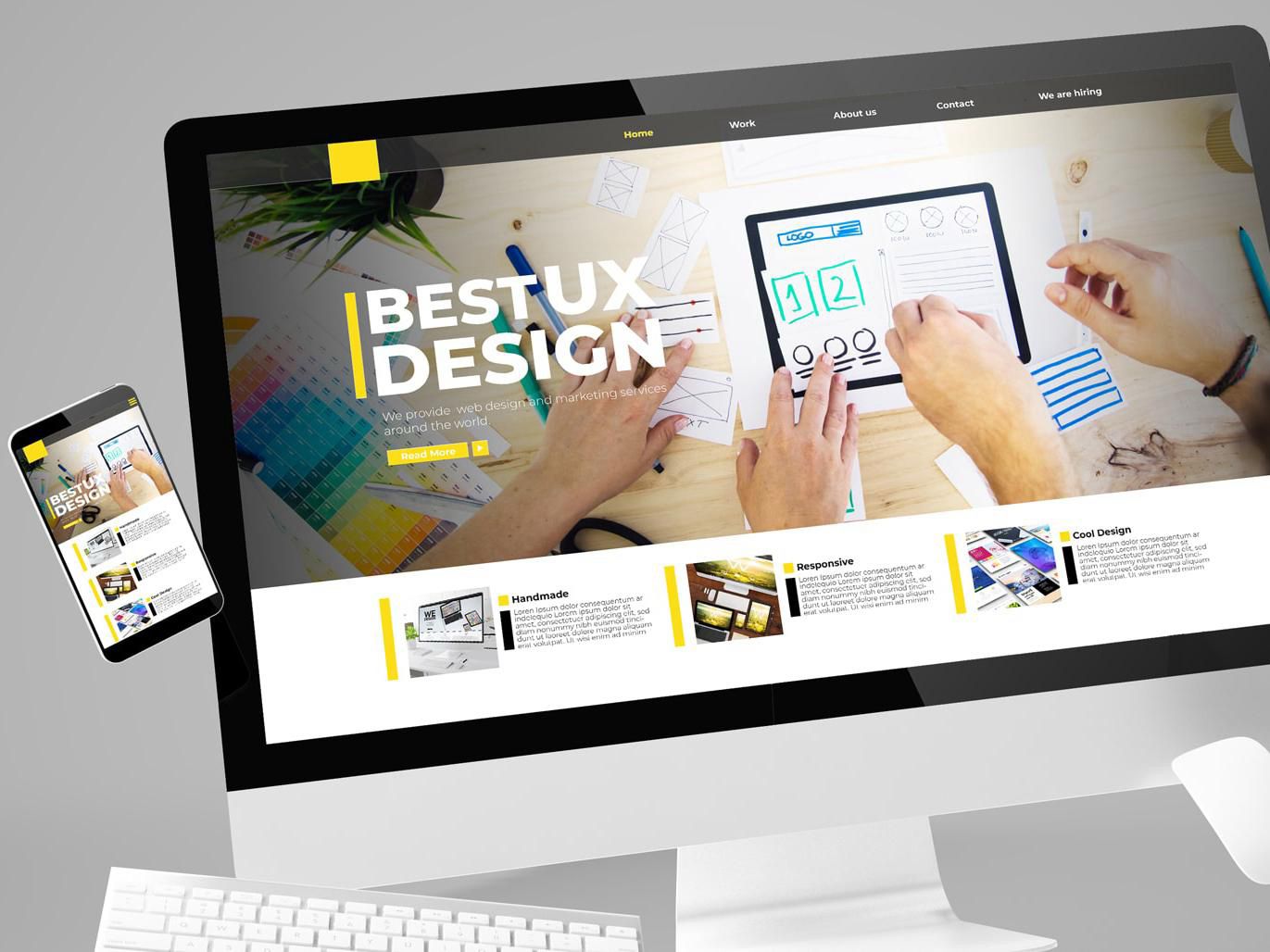
I can’t stress this enough—design isn’t just about pixels anymore. It’s about systems. Components. Design tokens. And underneath all that beauty lies the humble version control system.
You might think Git is just for developers. Nope. Today’s best design teams sync style libraries, track UI changes, and even version their Figma files using GitHub integrations. The benefits? Accountability. Revertability. Clean collaboration.
Globally, over 90 million developers use GitHub (GitHub Octoverse 2024 report), and tools like GitHub Copilot are making waves even in the design space—automating repetitive CSS snippets or helping designers write front-end logic without switching apps.
WDC has embraced this deeply. Their code repositories aren’t just storage lockers—battle-tested systems, tightly integrated with CI/CD pipelines, design systems, and QA checks. But here’s the thing: this level of organization might initially feel overkill for small businesses in South Carolina who aren’t used to such structure. That’s where good onboarding makes the difference.
Design Systems: From Atomic Design to Tailwind UI
Let’s go atomic—literally. Brad Frost coined the concept of atomic design, which has become the backbone of many scalable front-end frameworks. It’s all about building UI components as atoms (like buttons), molecules (like input fields), organisms (like contact forms), and so on.
It sounds nerdy—and it is nerdy—but it works. When appropriately implemented—often with tools like Storybook, Tailwind CSS, or Chakra UI—it helps keep design consistent across a website, even as it grows.
This philosophy is applied at Web Design Columbia even in small-scale projects. Why? Because even a 5-page site benefits from structure. Tailwind UI, in particular, helps WDC create consistent layouts with minimal CSS bloat. But not everyone loves Tailwind. Critics argue it clutters HTML with utility classes and makes handoff harder for beginners.
The truth? It depends on how it’s used. And with 20 years of design and coding knowledge under their belt, WDC knows exactly when to lean on it—and when to roll out good old-fashioned SCSS.
What Works in Chrome Might Break in Safari: Welcome to the Browser Olympics
Let me paint a picture for you. The final version of a freshly coded website is done. It looks phenomenal in Chrome, scrolls like butter in Firefox, and even Edge is playing along. But then someone tests it on Safari, and suddenly, buttons float, animations jitter, and font rendering goes rogue like it’s the early 2000s again.
This isn’t a rare occurrence. Despite CSS specs becoming more standardized, browser inconsistencies still give experienced developers headaches. Especially when animations or cutting-edge features are involved. And let’s not even talk about Internet Explorer—may it rest in peace, but its legacy bugs still haunt corporate intranets.
For a web design company in Columbia, SC, browser testing isn’t just a checklist—it’s a ritual. Web Design Columbia (WDC) uses tools like BrowserStack and LambdaTest to simulate dozens of environments, from the newest macOS Safari to Android Chrome on a mid-tier Samsung. While the average client might assume “if it works on my computer, it works everywhere,” the truth is far murkier.
This is also where things get tricky cost-wise. Comprehensive QA across browsers takes time. And for many agencies, that means extra billable hours. What WDC does differently—something I’ve admired—is bake testing into their workflow. It’s not an optional layer slapped on at the end. It’s a core part of every phase; somehow, they’ve managed to keep that affordable.
CI/CD for Design? Yes, That’s a Thing Now
Most people associate CI/CD (Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment) with DevOps pipelines, automated tests, and Kubernetes deployments. But here’s a secret: modern design also benefits from CI/CD.
Let’s say you’re working on a React app with a design system built in Storybook. Every commit that changes a button style or grid alignment can automatically spin up a preview site, run accessibility audits, and even push updates to internal staging environments. And if you think that’s overkill for your little bakery site in Columbia, South Carolina, think again—because it’s actually saving money in the long run.
WDC has quietly implemented these workflows, integrating GitHub Actions and Netlify Hooks to auto-build preview sites whenever changes occur. For clients, this means fewer surprises at launch. For designers, it means catching issues earlier. But CI/CD systems are only as good as those configuring them. Sloppy automation leads to bloated build times, broken assets, or even version mismatches. It’s not about having fancy tools—it’s about using them wisely.
And this is where that “almost two decades of experience” line suddenly becomes way more than marketing fluff.
Fonts, Files, and the Performance Trap
Let’s talk about speed. Not “my-site-loads-in-three-seconds” speed. I mean Lighthouse-obsessed, Core-Web-Vitals-optimized, users-don’t-bounce-in-anger speed.
According to Google’s benchmarks, sites that load in under 2.5 seconds have 32% lower bounce rates and more than double the conversion rate of slower competitors. So yes, performance is not just a developer’s vanity metric—it’s business-critical.
Yet many modern design tools encourage indulgence. You want a 3D hero image with animated text and ten Google Fonts? Go for it. But be prepared to watch your PageSpeed score cry. This is why performance tuning is just as much a part of the design process today as choosing the right color palette.
At WDC, the team trims unused JavaScript, lazy-loads assets, and yes, they even optimize your fonts (Google Fonts preload strategy, anyone?). They often make sites pass Lighthouse 90+ scores on first load—even with visual flair. This isn’t magic; it’s a practice grounded in discipline and tooling.
A web design company in Columbia, SC, doesn’t always get credit for leading in performance. Still, Web Design Columbia often outperforms big-city agencies in terms of raw efficiency, mostly because they don’t have layers of red tape slowing them down.
The Accessibility We’re Still Getting Wrong (and Why It Matters)
Here’s a fact that still surprises some clients: 15% of the world’s population lives with some form of disability (WHO). That’s over one billion people. Yet global studies consistently show that 96% of websites have basic accessibility failures—missing alt text, low contrast ratios, improper ARIA labels.
You might think, “But my site looks fine.” Sure, but can someone using a screen reader navigate it? Can someone with low vision adjust the font size without breaking the layout? Web accessibility isn’t just a “nice to have” anymore—it’s a compliance issue, a legal risk, and frankly, an ethical responsibility.
Web Design Columbia bakes accessibility into every project phase. They test color palettes against WCAG standards, structure headings semantically, and ensure smooth keyboard navigation. But there’s a catch. Accessibility tools like Axe DevTools and Lighthouse Accessibility audits are only part of the story. True accessibility requires empathy, iteration, and sometimes, re-education of both client and designer.
In one recent project, WDC even rewrote an entire navigation structure after live tests with screen reader users revealed flow issues. That’s the kind of deep care you don’t always get from larger firms outsourcing overseas. And yes, they still kept it affordable.
Is AI Coming for Web Designers? Not Exactly.
Let’s address the dragon in the room: generative AI. Tools like Wix ADI, ChatGPT plugins, and even Figma AI plugins are trying to democratize design, automating everything from layout decisions to actual code generation. Wix claims their ADI can build you a “stunning website in minutes.” Sounds great, until your site looks eerily like ten thousand others.
The truth is, AI is getting better fast. But it can’t replace context, nuance, or understanding your user’s weird and specific journey. Web Design Columbia has embraced AI tools for what they are: assistants, not replacements. They use them to generate content suggestions, refine alt text, or create placeholder layouts. But the final product is always human-refined.
In South Carolina and beyond, many businesses are learning that AI-designed sites often fail to meet performance, accessibility, and uniqueness standards. They end up turning to firms like WDC for help.
What Happens After Launch Matters More Than You Think
Let’s say your site is live. Hooray! But now comes the part most businesses forget—iteration. Web traffic needs to be monitored. Heatmaps reviewed. Conversions analyzed. What looks good on day one might perform poorly by day 30.
Design today is less like painting a portrait and more like running a café: you tweak the menu, adjust the lighting, and constantly respond to feedback.
WDC doesn’t just ship and vanish. Their teams often work with long-term clients to test new CTAs, adjust layouts for better conversion, and roll out seasonal updates. That’s a design philosophy rooted in business growth, not vanity metrics.
A web design company in Columbia, SC, with that kind of post-launch mindset isn’t just rare—it’s quietly becoming a local powerhouse for results-driven design.
Closing Thoughts (and a Word From the Field)
After digging through global design trends, testing dozens of tools, watching a few too many performance graphs, and listening to real feedback from Columbia business owners, I’ve come to a simple conclusion:
Good web design today is about balance.
while the flashy, billion-dollar tech companies might get the headlines, it’s often the quietly consistent, deeply experienced, and strategically humble agencies—like Web Design Columbia (WDC)—that actually deliver what clients need.
Suppose you’re curious about designing websites everyone loves, especially ones that respect your budget and still pack a performance punch. In that case, you might want to look in the most unexpected place: the charming and growing digital hub of Columbia, South Carolina.
Tech
cevurı: The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Its Impact

The term cevurı has gained increasing attention in recent years, yet its full implications remain underexplored. As a concept, it bridges multiple disciplines, offering unique insights into modern advancements. This article delves into the essence of cevurı, examining its origins, applications, and future potential. By understanding its role, readers can better appreciate its influence across various fields.
Origins of cevurı
The origins of cevurı trace back to early theoretical frameworks, where it was first conceptualized as a unifying principle. Initially, researchers struggled to define its boundaries, but over time, a consensus emerged. Today, it is recognized as a cornerstone of innovative thinking, shaping methodologies across industries.
Key Characteristics of cevurı
Several defining features distinguish it from related concepts. First, its adaptability allows seamless integration into diverse systems. Second, its scalability ensures relevance across small and large-scale applications. Finally, its predictive capacity enables forward-thinking strategies, making it indispensable in dynamic environments.
Applications of cevurı
The practical uses of it span multiple sectors. In technology, it drives algorithmic efficiency, while in business, it enhances decision-making processes. Furthermore, creative industries leverage it to foster originality, proving its versatility. Case studies demonstrate its transformative impact, solidifying its importance.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, it is not without challenges. Implementation barriers often arise due to resource constraints, and misinterpretations can lead to inefficiencies. However, ongoing research aims to address these issues, ensuring broader accessibility and effectiveness.
Future Prospects of cevurı
The future of cevurı appears promising, with emerging trends suggesting expanded applications. Experts predict advancements in AI and sustainability will further integrate it, unlocking unprecedented possibilities. Staying informed on these developments will be crucial for stakeholders.
Conclusion
In summary, cevurı represents a groundbreaking concept with far-reaching implications. From its origins to its future potential, understanding it is essential for anyone engaged in innovation. By embracing its principles, industries can unlock new opportunities and drive progress.
Tech
žižole: Exploring Its Significance and Modern Applications

The concept of žižole has emerged as a key driver of modern advancements, yet its full scope remains underexplored. Often associated with cutting-edge developments, žižole bridges gaps between theory and practical implementation. This article examines its origins, core principles, and real-world applications while highlighting its transformative potential. By the end, readers will gain a deeper understanding of why it is becoming indispensable across industries.
Origins and Evolution of žižole
The term žižole first appeared in early academic discourse, where it was used to describe a unique convergence of ideas. Initially, its definition was fluid, but over time, researchers refined its meaning. Today, it is recognized as a framework for innovation, blending creativity with structured problem-solving. Its evolution reflects shifts in technological and philosophical thought, making it a dynamic and adaptable concept.
Core Principles of žižole
Several fundamental principles define it. First, it emphasizes adaptability, allowing it to thrive in rapidly changing environments. Second, it prioritizes scalability, ensuring relevance across different contexts. Third, it fosters interdisciplinary collaboration, breaking down traditional silos. These principles collectively make it a powerful tool for modern challenges.
Applications of žižole in Technology
In the tech world, žižole has revolutionized approaches to artificial intelligence, data analysis, and system design. For instance, AI algorithms now incorporate it-inspired methodologies to enhance learning efficiency. Similarly, big data frameworks leverage its principles to improve predictive accuracy. As a result, industries ranging from healthcare to finance are adopting žižole-driven solutions.
žižole in Business and Strategy
Businesses increasingly rely on it to refine decision-making and strategic planning. Its emphasis on flexibility helps companies navigate market uncertainties. Moreover, it encourages iterative innovation, allowing firms to test and refine ideas quickly. Case studies from leading corporations demonstrate how it-driven strategies lead to sustainable growth.
Challenges in Implementing žižole
Despite its advantages, it presents certain challenges. Resistance to change often hinders adoption, particularly in traditional industries. Additionally, a lack of standardized guidelines can lead to inconsistent applications. However, ongoing research and collaborative efforts aim to address these barriers, paving the way for wider acceptance.
The Future of žižole
Experts predict that žižole will play an even greater role in shaping future innovations. Emerging fields like quantum computing and biotechnology are already incorporating its principles. Furthermore, as global challenges grow more complex, it problem-solving framework will become increasingly vital. Staying ahead of these trends will be crucial for professionals and organizations alike.
Conclusion
žižole represents more than just a theoretical concept—it is a practical tool driving progress across multiple domains. From its origins to its future potential, understanding it is essential for anyone engaged in innovation. By embracing its principles, industries can unlock new opportunities and stay competitive in an ever-evolving world.
-

 Blog3 months ago
Blog3 months ago鲁Q 669FD: Understanding Vehicle Registration in China
-

 Blog3 months ago
Blog3 months agoSwatapp.me المانجا: Your Gateway to the World of Manga
-
Tech6 months ago
IPv6 Internet Is Broken
-

 Tech2 months ago
Tech2 months agoWepbound: The Future of Web Development
-

 Tech6 months ago
Tech6 months agoScamalytics: Revolutionizing Scam Detection in the Digital Age
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoUnveiling adsy.pw/hb3: Revolutionizing Content Marketing Strategies
-

 Tech6 months ago
Tech6 months agoWebmxhd: Revolutionizing Digital Connectivity
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoprostavive colibrim Benefits, Uses, and How It Works
